What are the benefits of digitalizing bank guarantee management?
Trade finance encompasses strategies, financial instruments, and products that are essential for companies to facilitate international and domestic trading. Trade finance provides financing for trade, but also security in terms of granting bank guarantees for the trade. While enterprises tend to deal with hundreds if not thousands of guarantees yearly, the process for it is often fragmented and unnecessarily complex while lacking visibility into the full lifecycle of a guarantee.
As a result, enterprises are looking to improve the bank guarantee management process with solutions that can be integrated into the existing technology setup and allow all stakeholders to get appropriate user rights. Before explaining how a trade finance solution can help with digitalizing bank guarantees, we will walk you through the concept of trade finance and financial guarantees, the four pillars of trade finance, and finally how a software solution digitalizes guarantee management from the application to managing the granted guarantees.
What is trade finance and how does it work?
Trade finance is a process to finance commerce both domestically and internationally. The main trade finance instruments are trade credit, cash advance, purchase order (PO) finance, receivables discounting, term loans, export finance, and other types of business finance (e.g., equity financing, leasing and asset-backed financing, and asset financing). A trade transaction always requires a seller of goods or services and a buyer. Third parties, such as banks and financial institutions are often involved in the trade finance process by helping out with the above-described financial instruments as well as bank guarantees.
In the case of a guarantee, the third party helps to eliminate the payment risk and the supply risk while providing the buyer with accelerated receivables and the seller with extended credit. The third party typically provides the buyer with a letter of credit and makes the payment on behalf of the seller upon receiving a document of proof, such as a bill of lading.
Risk mitigation is often a primary goal
Trade finance goes beyond ensuring that the goods will be financed. One of the most important aspects of trade finance is risk mitigation and settling any conflicts between trading partners. The buyer usually wants to mitigate the payment risk from the seller and ensure security if, for some reason, they would not receive the goods or services, while the seller wants to mitigate the supply chain risk. To minimize the risk related to any trade, parties often need to apply for a guarantee from a bank to be able to move forward with the deal in a secure way.
What are the four pillars of trade finance?
When talking about trade finance we need to consider the concept of the four pillars of trade finance. The four pillars are payment, risk mitigation, financing, and provision of information. The pillars give a good overview of the basics of trade finance.
1. Payments
One of the primary roles of trade finance is to facilitate payments in a timely and secure manner internationally.
2. Risk mitigation
Another essential role of trade finance in international trade is to minimize risk for both trading parties. The types of risk that need to be mitigated are commercial risk (e.g., the seller does not perform its contractual obligations), country risk (e.g., financial crises), and currency risk (e.g., fluctuations in exchange rates).
3. Financing
Trade finance includes various forms of financing throughout the lifecycle of a trade deal, and it needs to be ensured that the financing instruments are versatile and flexible.
A few things that trade finance professionals need to think about are open accounts, supplier credits, advance payments, direct loans, credit documentation, collection documentation, export credit agency lending, factoring, and provision of information that trade finance professionals need to deal with.
4. Provision of information
Some trade finance experts argue that the provision of information is the most important area of trade finance as it ensures that all parties have access to accurate information throughout the entire lifespan of a transaction, minimizing the risk related to a lack of information or communication.
Trade finance and bank guarantees
From a treasury point of view, bank guarantees are a major factor in trade finance. They ensure that trading partners can work together while the financial risk is reduced to an absolute minimum. Nevertheless, the guarantee management process is often still cumbersome. To resolve the issues that are resulting from a fragmented, highly manual process, enterprises may use guarantee management solutions provided by the banks (usually supplied by a third-party provider) or opt for guarantee management SaaS solutions. Some enterprises may be tackling thousands of guarantees yearly, so having software and good processes in place becomes a must. Just recently we have published a list of the top trade finance software solutions to get a better picture of the available solutions out there.
What is a financial bank guarantee?
In trade finance, we talk about a bank guarantee when there is a third party (most often a bank) that agrees to pay a certain amount of money to the buyer upon the trading partner failing to deliver the goods within an agreed timeframe. The bank acts as a mediator and becomes the Guarantor as the Guarantee transfers the credit worthiness of the Applicant to the bank.
How exactly does a bank guarantee work?
When there is a breach of contract, for example, goods were not delivered, or the project was not completed according to the agreed terms, the guarantee starts to play a vital role in the trade. In this case, a Guarantor may pay the buyer a certain sum of money in line with the guarantee’s conditions. It’s important to emphasize that the Guarantor does not agree to complete the project or deliver the goods, simply, they will pay a fee that was agreed upon when signing the agreement and applying for a guarantee.
A guarantee is irrevocable: work with legal
Often, the Guarantor is third-party and thus completely independent from the parties participating in the trade, meaning that the Guarantor solely supports the transaction. When agreeing on a guarantee, it’s recommended to work with legal to ensure that the wording is correct, and that all parties agree to the terms and conditions of the guarantee deal. A guarantee is always irrevocable, meaning that once it’s been granted it cannot be amended or cancelled during the validity period without the consent of all the parties.
Guarantees are only drawn when the Applicant breaches the contract
It’s important to emphasize that the guarantee itself is a passive instrument and the Applicant (seller) and the Beneficiary (buyer) usually settle the underlying contract, the guarantee instrument is an additional document besides the contract. The guarantee is always valid until the expiration date that’s mutually agreed on by the parties and the instrument ensures the security of the Beneficiary upon trading with the Applicant.
How to digitalize bank guarantee management?
Now that we have covered the basics of trade finance and bank guarantees, it’s time to look at how a guarantee management solution can help digitalize the process. To explain how guarantees can be better managed in practice, we have relied on how Nomentia has been digitalizing the process for clients.
Manual trade finance processes are still a reality
In some countries, the guarantee management process can still be paper-based or often, guarantee applications are sent back and forth by email between the different stakeholders, such as subsidiaries, project managers, group treasury, legal, and more.
The inefficient guarantee application process
The cumbersome process can sound simple: the subsidiary applies for a guarantee, fills in a form and sends it by email to the group treasury for acceptance and signature so that it can be forwarded to the bank.
In reality, the process is often a lot more complex than that. During the review process, questions, modifications or rejections may arise from multiple stakeholders from different departments and in that case, the application form is sent back and forth by email. In certain cases, such as with large investments, the Group CFO may also need to accept the application. Once the guarantee is accepted, it’s often delivered to the bank either by email or by mail.
This process is already inefficient and time-consuming during the application phase – and now we are just considering one application. Some treasury departments can deal with hundreds of guarantee applications yearly and we haven’t yet considered what happens once the guarantee has been approved. Even once a guarantee is accepted, the process continues as records need to be maintained. For example, documents and certificates need to be stored and corresponding fees need to be administered.
The three elements of a guarantee workflow
A guarantee workflow can be divided into three major parts:

1. Internal request
A subsidiary submits a request to the group treasury or the trade finance team and the guarantee application process kicks off.
The application is filled out but may need to be edited later, or comments, as well as attachments, may still need to be included.
2. Internal review process
The group treasury or the trade finance team starts to handle the application. At this point, they may need to ask questions, or they may have requests or modifications, such as asking for missing attachments. Before approval, the team also needs to allocate a line of credit. At the end of the process, the guarantee is accepted or rejected.
3. External request
If the guarantee is accepted, it needs to be signed and sent to the bank. Typically, signing is paper based, and either the document is scanned and sent by email or sent as a letter to the bank.
How to optimize the guarantee application process using workflows?
The task sounds simple, and the workflow only consists of three main process steps. What’s the catch? Yet, for some companies it needs to work for hundreds if not thousands of guarantees. In such cases, the traditional way of handling guarantees becomes unfeasible.
Nomentia’s Trade Finance solution is a single place for managing all guarantees throughout the entire lifecycle, including managing the application process, sending the document to the bank, waiting for the approval to the banking, moving the guarantee under the active guarantees and even reporting.
Let’s take a deeper look at the Nomentia Trade Finance solution for guarantee management:
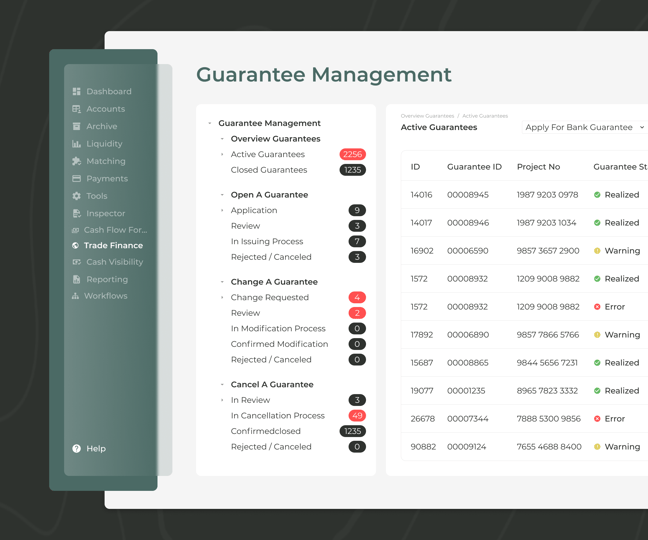
When you open the application, you will have a full overview of all your guarantees under the Guarantee Management tab. The be more exact, you can view the following:
- Overview
- Active guarantees
- Closed guarantees
- Open a guarantee
- Application
- Review
- In issuing process
- Rejected / canceled guarantee applications
- Change a guarantee
- Change requested
- Review
- In modification process
- Confirmed modification
- Rejected / canceled modification
- Cancel a guarantee
- In review
- In cancellation process
- Confirmed closed guarantee
- Rejected cancellation processes
How can you manage bank guarantees in Nomentia Trade Finance?
In the Overview module, you will be able to see all active guarantees and all closed ones that already expired and dig deeper into the data.
Active bank guarantees have further sub-processes such as active bank guarantee in modification, active bank guarantee in dunning/closing, and active corporate guarantees. Whenever you need to look for a specific guarantee you can get a full overview of all the guarantees and filter them by IDs, project IDs and other details like maturity or amount among others, just like you would be able to do in excel. In addition to this, all guarantees have a history log, so you can see what changes were made at which stage by which user.
In opening a guarantee, users can apply for a bank guarantee, surety, export L/C, corporate guarantee or record an external guarantee. Users can fill in the application and edit it and add comments before it is sent for review to the adequate team. Once the treasury or trade finance team reviewed it, they can either move the guarantee to the issuing process if there are no further questions or it can be rejected. If there are questions from treasury, the guarantee may move to the ‘Change a guarantee’ process and wait for modifications.
Subsidiaries can also cancel or close the guarantee or reject the cancellation process.
Guarantees and the issuing process
Once the group treasury or the trade finance team has accepted the guarantee, it’s going to go through the issuing process. The first step is to sign the guarantee application directly through the platform which can be integrated with solutions such as DocuSign, AdobeSign, or any other signature provider via an API connection so that the form can be easily signed digitally. Once you have signed the document, it can be saved and it’s ready to be sent to the bank either via email or through a bank connection.
After sending the application to the bank, users will see the “waiting for the bank” status message next to the application. Once the bank has granted the guarantee, the status is changed to “certificate approved” and the guarantee will move to the active guarantees.
Completely customizable guarantee process
The guarantee opening process will take into consideration the structure you have in place and the setup will completely depend on your organization’s processes. We can set up different user rights to make sure that all relevant stakeholders get notified only when they need to act. Users can only see what’s included as part of their user rights, which also applies to the list of guarantees and history logs.
This workflow-based solution can be completely tailored to the client’s unique needs. Some organizations, for instance, require a four-eyes principle while others may require an eight-eyes principle for, for example, a transaction worth more than 5 million EUR. The case-by-case customization of workflows allows us to streamline each customer’s guarantee management process in line with their treasury policies so that they can digitalize the entire process.
When you are using the system, you can also integrate it with almost any other system you are using, so you won’t need to manually export and import any data.
Guarantee reporting
When you are working with guarantees, you need to do a lot of reporting. All types of reports can be exported to excel or Nomentia Reports, like guarantee engagement, counterparty reports, detail reports, external guarantee invoices, and internal guarantee invoices.
Improve your guarantee management process
Guarantee management will remain an important aspect of many companies’ trade finance processes and looking into solutions that make the management of guarantees easier may be interesting for you. In another article, we have looked at some of the best trade finance software on the market – make sure you check out that article as well.




.png?width=980&height=200&name=guarantee%20management%20-%20banner%20(1).png)

