How should companies prepare for building a payment factory?
Preparation starts with assessing current payment processes, identifying inefficiencies, and defining project objectives. Success depends on engaging stakeholders early, aligning IT and finance, and setting clear functional and technical requirements. This ensures smoother implementation, stronger compliance, and long-term scalability.
A payment hub offers organizations a centralized platform to streamline payment processes and enhance financial management, especially in complex payment landscapes. As forward-looking treasury and cash management professionals increasingly adopt these systems to safeguard and future-proof business-critical operations, proper preparation becomes essential for success.
Building a payment factory requires careful planning to ensure alignment with organizational needs, seamless integration with existing systems, and delivery of stakeholder benefits. Preparation not only mitigates risks and minimizes disruptions but also maximizes the success of the implementation.
Here's a comprehensive checklist for organizations planning to build a payment factory:
1. Assessing your current payment processes

Evaluate existing payment workflows and processes:
Before embarking on your payment factory journey, it is vital to understand what’s beneath your current payment operations, and what’s behind the processes. Things like what systems you have in place, how many bank accounts you have, where your payment files are located, which banks you work with, and how much your processes differ based on locality. Start by assessing your current payment processes to understand how payments are currently managed, the systems in place, and any pain points or inefficiencies.
Identify pain points and areas for improvement:
Identify bottlenecks, manual processes, errors, and inefficiencies in your current payment workflows. You should account for the fact that operating across borders can require finding a balance between centralization and local autonomy. For further understanding, read this article.
Determine the scope and objectives of the payment factory project:
Define the scope of the payment factory project, including its objectives, goals, and expected outcomes. Check out this article discussing payment hub scope and objectives.
2. Engaging stakeholders in payment factory project
Identify key stakeholders:
Identify key stakeholders, including finance, IT, procurement, and executive leadership, who will be involved in the payment factory project. Make sure that you have buy-in from all the stakeholders and you will have clear roles and responsibilities going forward once the project kicks off.
Communicate project goals and objectives:
Clearly communicate the goals, objectives, and expected benefits of the payment factory project to all stakeholders. Communication is perhaps the most difficult part of the project. Managing change is never easy as some of customers can testify.
Earn buy-in and support:
Gain buy-in and support from stakeholders by demonstrating the value of the payment factory and addressing any concerns or objections.
Cross-functional project team:
Establish a cross-functional project team to oversee the implementation, with representatives from finance, IT, procurement, and other relevant departments. While it may be the finance team that will be the main user of the payment solution, other departments could also be affected. Make sure you take it into consideration from the beginning. The IT and security departments will be your biggest stakeholders as you will need to team up with them to ensure that the payment factory project is delivered, and the solution meets all compliance expectations.
3. Setting clear objectives and requirements for the implementation

Define objectives and goals:
Clearly define the objectives and goals of the payment factory project, like improving efficiency, reducing costs, enhancing control, and minimizing risks. Best payment factory objectives and goals are always aligned with wider organizational business goals. While some seek to be more compliant, others want to put in place uniform global processes, but in the end, all share a common drive to enable their teams to work better together while improving transparency.
Specify functional and technical requirements:
Specify the functional and technical requirements for the payment factory based on the organization's needs and objectives. For example, the system should automate the end-to-end payment process, including payment initiation, validation, authorization, and execution while providing real-time reporting and analytics on payment transactions, which enables your organization to monitor cash flows, identify trends, and make informed decisions quickly. On a technical level, these requirements could include things like integration with ERP and financial systems while supporting high availability and scalability.
Prioritize requirements:
Prioritize requirements based on their importance to the business and their impact on achieving project goals. When prioritizing requirements for payment factories, you should consider the strategic objectives, geographic focus, and operational complexity of your operation. For example, a company looking to streamline operations in a specific region should prioritize setting up the payment factory in that location first. This requires them to focus on local compliance, integrating with regional banks, and automating processes to enhance efficiency. Once the initial implementation is successful, the company can then expand to other countries, scaling the system to handle additional bank connections and accounts. By starting small and gradually expanding, businesses can manage system complexity effectively and ensure a smooth transition to an optimized, centralized payment process.
Document requirements:
Document requirements in a detailed project plan or specification document to guide the implementation process. The right partner can help organizations identify their payment factory needs by leveraging their expertise to conduct thorough assessments and gap analyses. They can also assist in crafting a comprehensive RFI/RFP that captures all critical requirements, ensuring that once the scoping of the project begins, the implementation is aligned with the organization's strategic goals and operational needs.
4. Selecting payment factory vendor or solution
Research available solutions and vendors:
Research available payment factory solutions and vendors to identify those that best meet your requirements. Collaborating with an experienced partner can streamline this process, as they can provide valuable insights into the strengths and weaknesses of various solutions based on your specific needs. Additionally, they can facilitate vendor evaluations and comparisons, ensuring that you select a solution that aligns perfectly with your operational goals and technical specifications.
Evaluate vendors:
Evaluate vendors based on criteria such as functionality, scalability, integration capabilities, cost, and reputation. It's crucial to align this evaluation with the company's original plan, ensuring that the chosen vendor can meet the specific requirements and strategic objectives outlined from the outset. By maintaining a clear focus on the initial project plan, businesses can ensure that the selected solution not only fits current needs but also supports future growth and operational goals.
Request proposals or demos:
Request proposals or demos from shortlisted vendors to assess their capabilities and suitability for your organization. Ensure all necessary stakeholders are present during these demos to gather diverse perspectives and keep everyone informed. Additionally, prepare thoroughly for these demos by outlining key evaluation criteria and questions in advance, allowing you to effectively compare vendor capabilities and make a well-informed decision.
Select the best vendor:
Select a vendor that best meets your needs and objectives, considering factors such as functionality, cost, support, and reputation. Ensure the vendor can support the languages and geographical locations relevant to your business operations and planned expansion. Assess their ability to establish and manage bank connections, focusing on how these integrations will be set up and maintained. Additionally, evaluate their IT support services, including availability, response times, and how they will collaborate with your organization to ensure seamless implementation and ongoing support. This comprehensive approach will help ensure the chosen vendor aligns perfectly with your strategic goals and operational requirements.
5. Creating a project plan
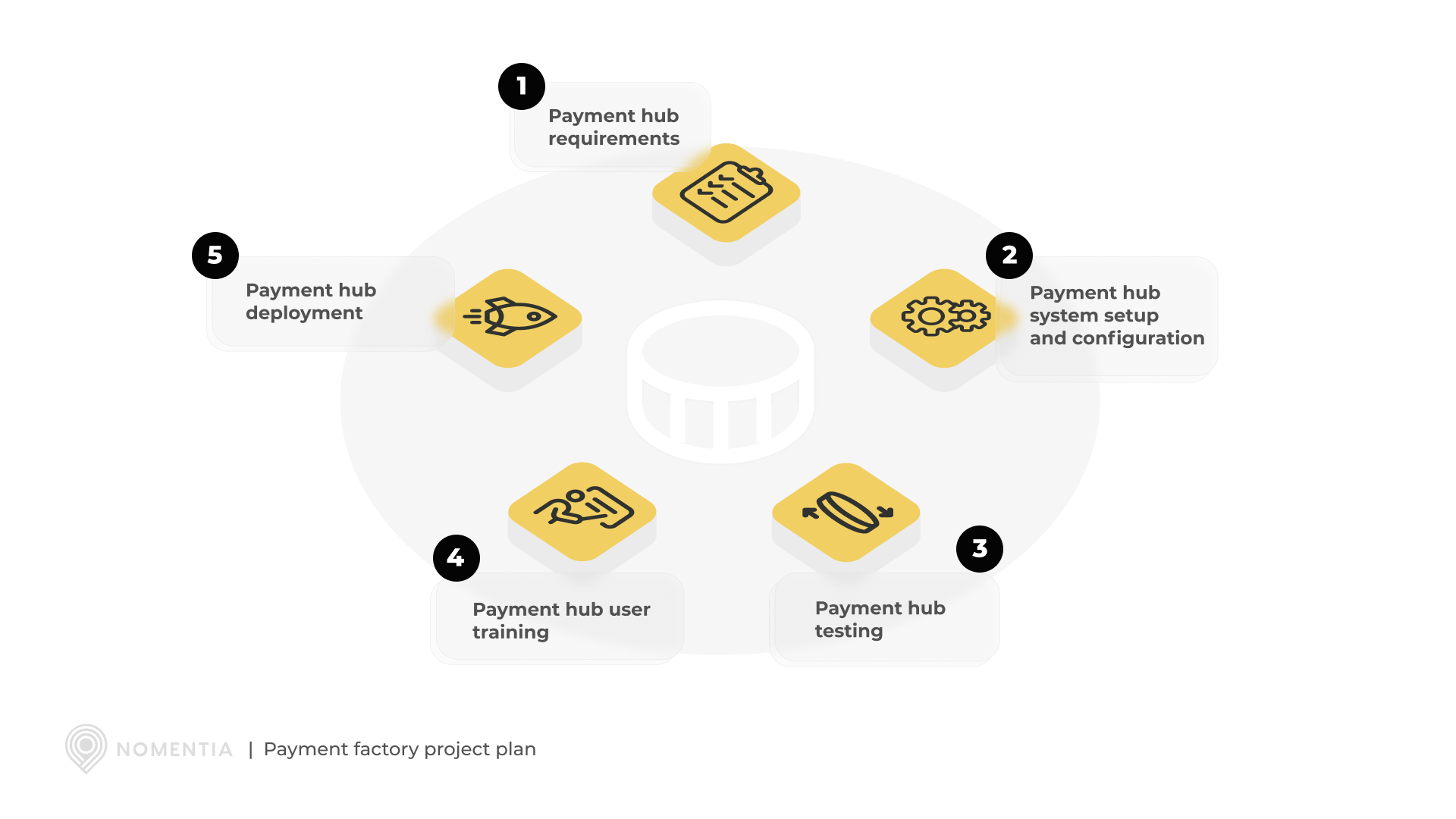
Develop a detailed project plan:
Start by developing a comprehensive project plan that outlines the entire implementation process of the payment factory. This plan should include detailed timelines, key milestones, deliverables, and specific tasks required at each stage of the project. By clearly mapping out these elements, you can ensure that all team members understand the project's scope and deadlines, facilitating smoother execution and progress tracking.
Assign responsibilities:
Next, assign clear responsibilities to each team member and stakeholder involved in the project. Define who is accountable for specific tasks, ensuring that everyone knows their roles and duties within the project. This clarity not only helps in maintaining accountability but also enables efficient task management and coordination, preventing overlaps and gaps in the workflow.
Establish communication channels:
Establish robust communication channels and protocols to keep everyone informed and engaged throughout the project. Set up regular updates, feedback loops, and mechanisms for issue resolution to ensure timely communication and address any concerns promptly. Effective communication is crucial for payment factory project success, as it helps in synchronizing efforts, sharing progress, and making informed decisions collaboratively.
6. Training and change management
Ensure a training plan:
Start by developing a comprehensive training plan for end-users and stakeholders to ensure they understand how to use the payment factory effectively. This plan should detail the training schedule, methods, materials, and specific objectives for each training session. By providing clear and structured training, you can ensure that all users are well-prepared to utilize the new system, minimizing disruptions and enhancing productivity.
Provide training:
Implement the training plan by providing thorough training sessions on new payment processes, workflows, and system functionalities to all users. This training should be hands-on and tailored to the specific needs of different user groups, ensuring that everyone gains the necessary skills and knowledge to operate the payment factory efficiently. Ongoing support and refresher training should also be included into the project to reinforce learning and address any emerging questions or issues.
Address concerns and resistance to change:
Address concerns and resistance to change through effective change management strategies: communicate, educate, and involve people as much as you can. Engage with stakeholders regularly to understand their apprehensions and provide clear, transparent information about the benefits and impact of the new system. Involving users in the implementation process and offering continuous support can help ease the transition and foster a positive attitude towards the change.
Foster a culture of continuous improvement:
Fostering a culture of continuous improvement and learning encourages the adoption of the payment factory and ongoing optimization of processes. Promote feedback mechanisms where users can share their experiences and suggest improvements. By encouraging a mindset of ongoing development and refinement, you can ensure the payment factory remains effective and adapts to evolving business needs, ultimately leading to sustained operational excellence.
7. Go-live and post-implementation support
Plan and execute the go-live process:
Plan and execute the go-live process for the payment factory, ensuring a smooth transition from existing systems. Begin by developing a detailed go-live plan that outlines all necessary steps, including final system checks, data migration, and user readiness assessments. Ensure that there is a clear schedule and a checklist of tasks to be completed, with designated responsibilities and timelines for each action item to guarantee a structured and coordinated rollout.
Monitor system performance:
Monitor the performance of the payment factory and address any issues or concerns to ensure optimal operation. To ensure a smooth transition and minimize disruptions, plan to operate both the existing systems and the new payment factory concurrently for a defined period. This dual-system approach allows you to identify and address any issues that arise in real time without halting operations. By monitoring performance and gathering feedback from users during this period, you can make necessary adjustments and ensure that the new system is fully functional and reliable before completely phasing out the old system.
Review and Optimize Post-Go-Live
After the go-live process, conduct a thorough review to assess the performance of the payment factory and identify any areas for improvement. Gather feedback from users and stakeholders to understand their experiences and any challenges they faced. Use this information to make necessary optimizations and enhancements, ensuring that the system continues to meet the organization's needs and deliver expected benefits.
Preparing for a payment factory
By following this checklist and adequately preparing for building a payment factory, organizations can streamline their payment processes, enhance control and visibility, and achieve their financial management objectives effectively.
Frequently asked payment factory questions (FAQ)
How to set up a payment factory?
How do you choose the right technology or platform for a payment factory?
What are the usual challenges faced during the implementation of a payment factory, and how can they be overcome?
How can a payment factory improve cash flow management?
A payment factory is a must for forward-looking payment operations. Centralization consolidates payment processes, giving you a comprehensive view of cash flows across the organization for better forecasting and management. Efficiency comes from automating payments, reducing processing time and errors, ensuring timely payments and receipts. Enhanced control over payment schedules and terms helps manage liquidity more effectively. Additionally, a payment factory can help you to negotiate better terms with banks and service providers, optimizing cash flow positions.
What is the role of analytics in a payment factory?
Analytics are a crucial part of payment factories. They provide real-time insights into payment activities, helping identify trends and anomalies through monitoring and reporting. Analytics also support data-driven decision-making to optimize payment processes and manage cash flows. Additionally, analytics helps detect and prevent fraudulent activities by identifying unusual patterns and behaviors.
How can a payment factory enhance compliance with global payment regulations?





